Guadeloupe topographic map
Interactive map
Click on the map to display elevation.
Guadeloupe
The two main islands are Basse-Terre (west) and Grande-Terre (east), which form a butterfly shape as viewed from above, the two 'wings' of which are separated by the Grand Cul-de-Sac Marin, Rivière Salée [fr] and Petit Cul-de-Sac Marin. More than half of Guadeloupe's land surface consists of the 847.8 km2 Basse-Terre. The island is mountainous, containing such peaks as Mount Sans Toucher (4,442 feet; 1,354 metres) and Grande Découverte (4,143 feet; 1,263 metres), culminating in the active volcano La Grande Soufrière, the highest mountain peak in the Lesser Antilles with an elevation of 1,467 metres (4,813 ft). In contrast Grande-Terre is mostly flat, with rocky coasts to the north, irregular hills at the centre, mangrove at the southwest, and white sand beaches sheltered by coral reefs along the southern shore. This is where the main tourist resorts are found.
About this map
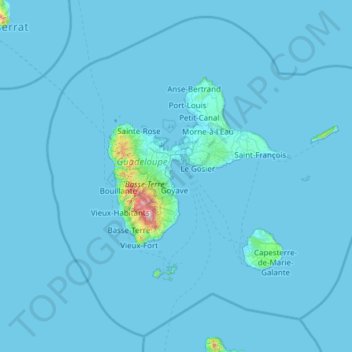
Name: Guadeloupe topographic map, elevation, terrain.
Location: Guadeloupe, France (15.64441 -62.01804 16.71400 -60.79197)
Average elevation: 18 m
Minimum elevation: -1 m
Maximum elevation: 1,428 m
Other topographic maps
Click on a map to view its topography, its elevation and its terrain.
Mont Blanc / Monte Bianco
France > Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes > Upper Savoy > Chamonix-Mont-Blanc
The climate is cold and temperate (Köppen climate classification Cfb), and is greatly influenced by altitude. Being the highest part of the Alps, Mont Blanc and surrounding mountains can create their own weather patterns. Temperatures drop as the mountains gain in height, and the summit of Mont Blanc is a…
Average elevation: 4,092 m
Les Résidences
France > Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes > Puy-de-Dôme > Murat-le-Quaire
Average elevation: 1,072 m
Siaugues-Saint-Romain
France > Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes > Haute-Loire > Siaugues-Sainte-Marie
Average elevation: 951 m
Les Baux
France > Pays de la Loire > Loire-Atlantique > Vair-sur-Loire > Saint-Herblon
Average elevation: 50 m
Tré-le-Champ - le Haut
France > Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes > Upper Savoy > Chamonix-Mont-Blanc
Average elevation: 1,737 m
Aix-en-Provence
France > Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur > Bouches-du-Rhône > Aix-en-Provence
Average elevation: 279 m
La Grave de Peille
France > Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur > Maritime Alps > Peille
Average elevation: 400 m
Paris
Paris in its early history had only the rivers Seine and Bièvre for water. From 1809, the Canal de l'Ourcq provided Paris with water from less-polluted rivers to the north-east of the capital. From 1857, the civil engineer Eugène Belgrand, under Napoleon III, oversaw the construction of a series of new…
Average elevation: 75 m
La Pierre de Neuvic
France > Nouvelle-Aquitaine > Haute-Vienne > Neuvic-Entier > La Pierre de Neuvic
Average elevation: 387 m
Le Revest-les-Eaux
France > Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur > Var > Le Revest-les-Eaux > Le Revest-les-Eaux
Average elevation: 327 m
La Pommeraye
France > Bourgogne – Franche-Comté > Saône-et-Loire > Beaurepaire-en-Bresse
Average elevation: 210 m
Pierrefitte-Nestalas
France > Occitania > Hautes Pyrenees > Pierrefitte-Nestalas > Pierrefitte-Nestalas
Average elevation: 712 m
Le Grand Morétan
France > Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes > Saint-Colomban-des-Villards
Average elevation: 2,306 m
Prairie
France > Hauts-de-France > Cuignières
Certain extraordinary features were produced when the retreat of the ice sheet had progressed so far as to open an eastward outlet for the marginal lakes. This outlet occurred along the depression between the northward slope of the Appalachian plateau in west-central New York and the southward slope of the…
Average elevation: 136 m
Les Petites Fourches
France > Bourgogne-Franche-Comté > Saint-Brisson > Les Petites Fourches
Average elevation: 629 m
